2010 Human adipose-derived stem cells current challenges and clinical perspectives
Samira Yarak, Oswaldo Keith Okamoto
Abstract: Adult or somatic stem cells hold great promise for tissue regeneration. Currently, one major scientific
interest is focused on the basic biology and clinical application of mesenchymal stem cells. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells share similar characteristics with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, but have some advantages including harvesting through a less invasive surgical procedure. Moreover, adipose tissue-derived stem cells have the potential to differentiate into cells of mesodermal origin, such as adipocytes, cartilage, bone, and skeletal muscle, as well as cells of non-mesodermal lineage, such as hepatocytes, pancreatic endocrine cells, neurons, cardiomyocytes, and vascular endothelial cells. There are, however, inconsistencies in the scientific literature regarding methods for harvesting adipose tissue and for isolating, characterizing and handling adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Future clinical applications of adipose tissue-derived stem cells rely on more defined and widespread methods for obtaining cells of clinical grade quality. In this review, current methods in adipose tissue-derived stem cell research are discussed with emphasis on strategies designed for future applications in regenerative medicine and possible challenges along the way.
CONCLUSION
Despite great advances, many important issues about the use of ADSC in tissue bioengineering remain unclear. These questions must be explored before clinical tests to better direct clinical strategies.
Among the greatest current challenges, we may cite: how to control the processes of proliferation and differentiation of ADSC in vitro and in vivo? Which factors control these processes? Which niche factors determine the control of its behavior? Which factors stimulate the migration to and integration of ADSC into the sites of tissue injury? What capacity do ADSC have to form tumors?
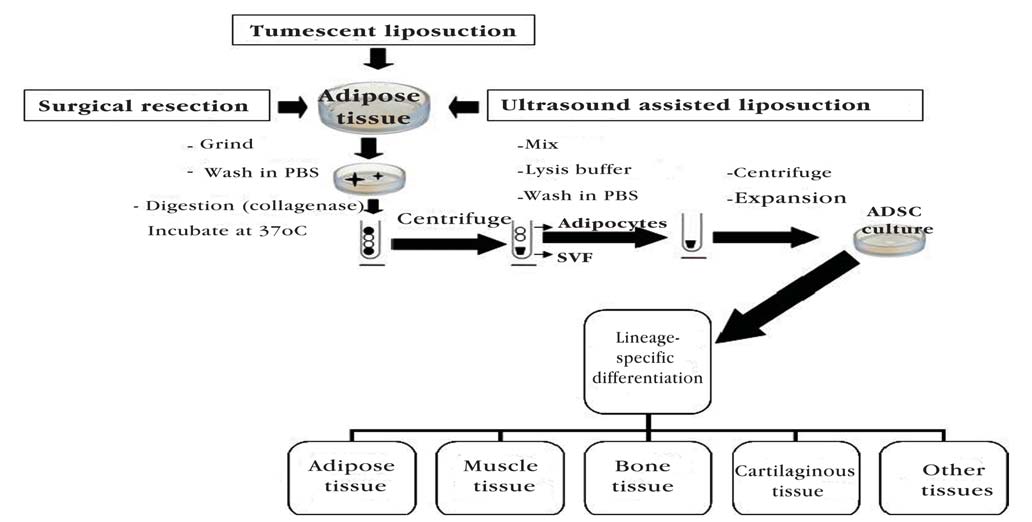
An important factor to improve ADSC research is the standardization of surgical and laboratory methodsused to isolate and characterize these cells. Along these lines, comparative studies are extremely relevant and should be conducted to evaluate surgical procedures employed to obtain adipose tissue and to locate the best adipose tissue donor area. Laboratory techniques for tissue preparation to isolate and identify ADSC, cell culture techniques in scale and purity degrees for clinical application, and the methods that evaluate the quality of the cells to be implanted (e.g. evaluation of cell differentiation potential, presence of genetic or epigenetic alterations, etc) should also be standardized.
The comprehension of the molecular mechanisms that regulate the self-renewal and differentiation of ADSC, as well as their interaction with the cell niche, is equally relevant. This basic knowledge may help the development of new therapies and the evaluation of biosecurity issues in future clinical protocols.
Key words: Adipocytes; Adipose tissue; Adult stem cells; Tissue therapy
Source : ┬®2010 by Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia
